
333
mum allowable crack sizes before the procedure on when and how to repair cracks in
welded joints was proposed. The most important conclusion of the study is that “fracture
mechanics analysis is acceptable basis for allowable exception from valid standards
under circumstances, under condition that this analysis provides clear and conservative
structural integrity assessment”. Just to mention that similar approach can be applied in
the case of nano materials.
The significance of detected or assumed crack in a structural component can be
assessed by FM approach, applying developed procedures, e.g. SINTAP /17, 18/.
3. SCALE EFFECT AT THE CRACK TIP
Crack tip region requires special attention, as can be concluded referring to Figs. 3 to 6. It
is also to underline that the model in Fig. 6 is based on many assumptions and simplification
regarding structure of material, and it is easy to recognize how far from reality applied model
is by comparing with fractograghs in Fig. 12. More close insight at the crack can help in this
situation.
The scale range within which continuum mechanics theories are applied is very nar-
row. All material properties differ when they are averaged over individual regions within
each grain that can be traced to crystal lattices. In addition, when load is applied, pre-
existing defects and imperfections can change their morphologies that can further add to
the complexities of the analyses. As the scale size is reduced, these changes can occur
continuously such that equilibrium may never be reached and the process is said to be in
non-equilibrium. The use of ordinary continuum mechanics theories that assume equilib-
rium and material homogeneity fails.
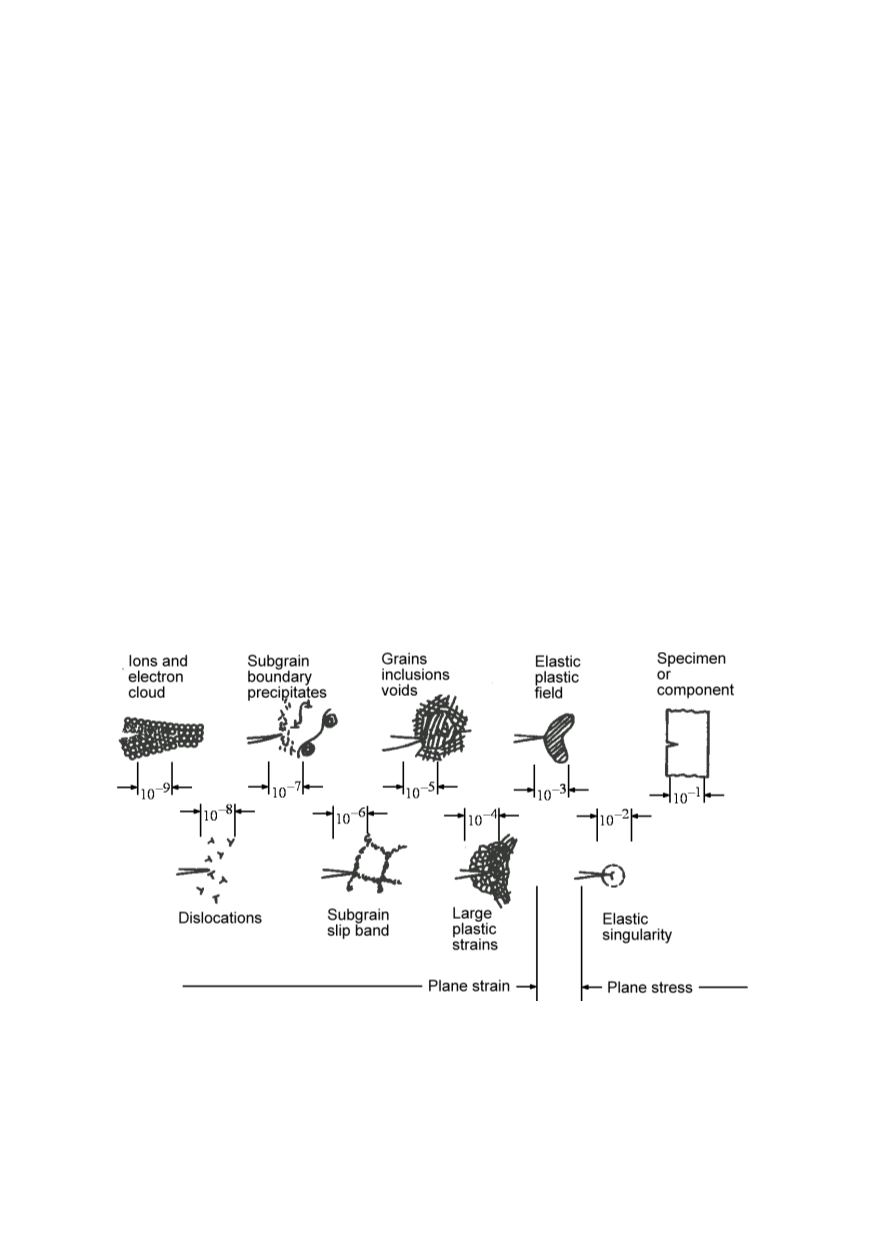
Initially considered phenomena at the crack tip related to crack propagation within
classic picture of metal structure are given in Fig. 13.
Figure 13: The sizes of phenomena in metals – a classical picture, presented in cm
Most important is that basic fracture mechanics formulae are developed for
continuous and homogeneous material, and the consideration at the atomic force level
just helped to confirm the applicability of obtained results, Fig. 6, Eq. (4), Eq. (7). The
size of edge dislocations is about 10
-8
cm, of sub-grain slip band 10
-6
cm, while large


















