
338
loaded material behaviour. However, it is not easy to imagine crack tip as a point in Figs.
4 and 6, but also in Fig. 13 at magnification higher than micro level. For that the validity
of applied formulae at macro scale is limited by the size of a structure, and simplifica-
tions of models in structural integrity and reliability analysis must be respected.
Development and introduction of nano materials and nano structures accentuate the
necessity to assess the integrity and consider the effect of defects, since their application
requires high level of reliability /22/. Important benefit of nano materials is high strength,
achieved by perfect arrangement of atoms. Due to size effect failure consequences are
different on macro/micro levels of that on nano level. The nano structure size is of
similar order of magnitude as crack tip region considered at macro-scale (Fig. 16). The
accuracy of the assessment of nano structure integrity is questionable having in mind that
atomic distance in crystal is small (≈ 0.5 nm) and the defect (crack) can be also small
(e.g. 10 nm).
5. DAMAGE AND FAILURE IN NANO STRUCTURES
Security and reliability of nano structures is of an utmost importance, because their
damages and failures might be of catastrophic consequences. Complexity of this problem
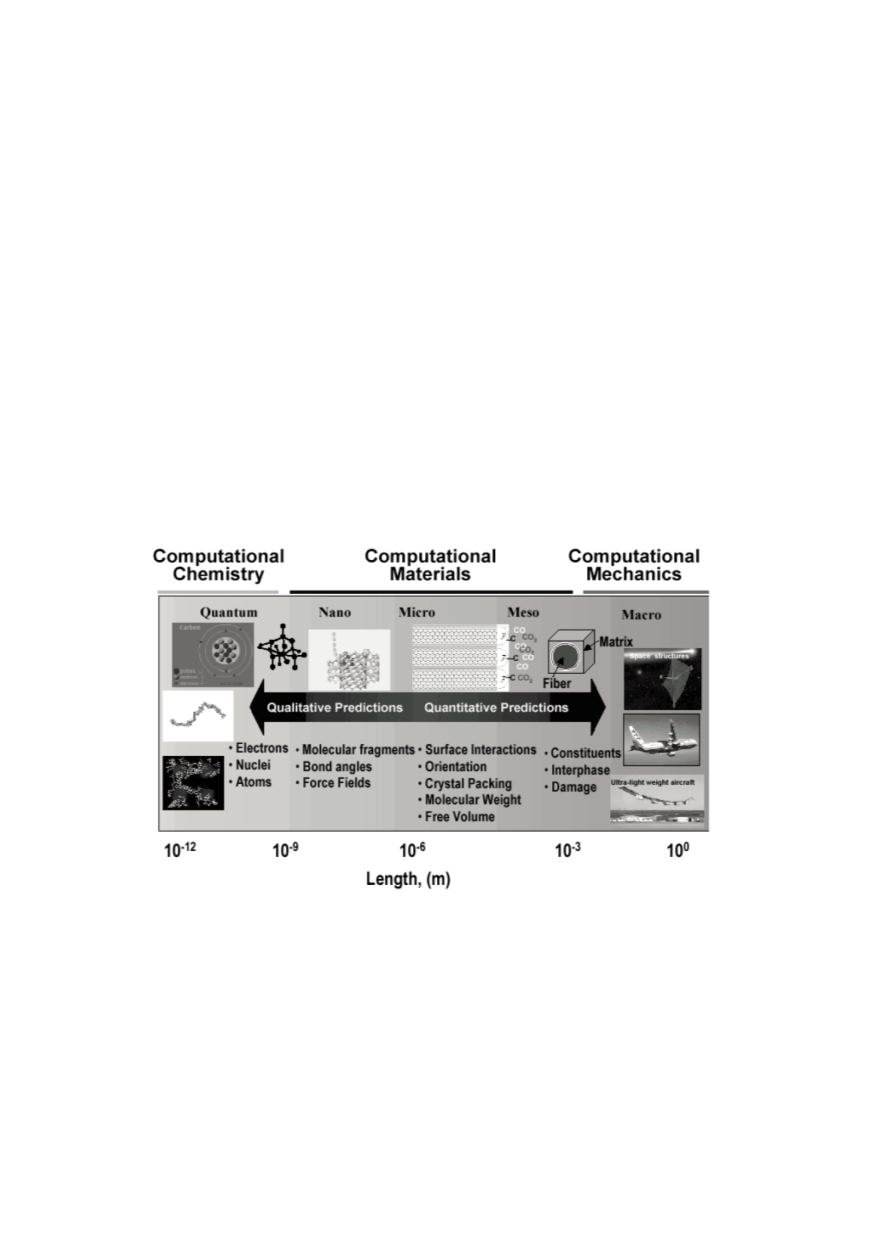
can be recognised from the scheme (Fig. 17) of computational modelling procedure /23/.
Anyhow, modelling of nano materials and nano structures is an inevitable step in
modern procedures for development and improvement, with significant effects.
Figure 17: Length and time scales in material modelling /23/
5.1. Hierarchical integrated simulation models
Hierarchical simulation approach integrates information obtained from more detailed
smaller-scale models into coarse-patterned, larger-scale models /1/. This approach has
been proved successful when the physics at different scales are weakly coupled. It is
feasible when, towards larger-scales, the information is passed via one or few common
parameters, like inter-atomic potentials on molecular dynamics/quantum mechanics
(MD/QM) interface, virtually decoupled from smaller-scale models. This is the base of
so-called “ab-initio” method, which enabled to develop convenient algorithms, appli-


















