
331
Sharp initial crack
Crack blunting
Crack growth in
plastic region
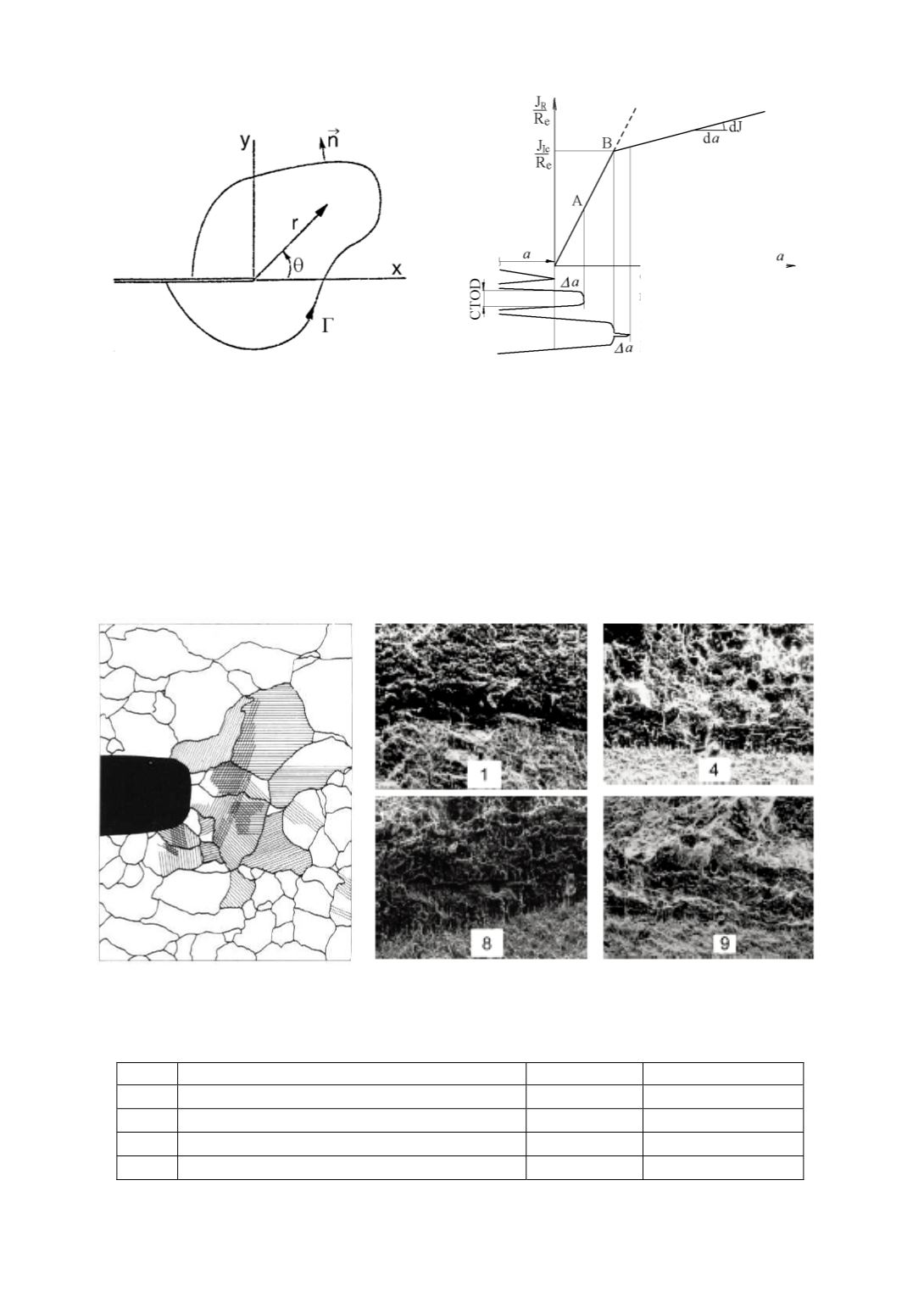
Figure 9. Arbitrary contour path for
J
integral Figure 10. Stable crack growth defined by J integral
When a large stretch zone at crack tip is developed, the crack-opening stress must
exceed the yield stress to cause plastic fracture and stable crack growth. If a small degree
of crack tip blunting is developed, the fracture is of elastic-plastic type. The elastic term
signifies that the fracture is developed for elastic crack-opening stresses, up to the point
B in Fig. 10, which indicates the final stretch zone, next FM parameter. Figure 11
illustrates that the crack tip blunting is the result of plastic slip within the grains. That is,
slip is developed prior to micro cracking of the grains. In the case of welded joint dif-
ferences in fractograms (Fig. 12) indicate the complexity of the problem.
Figure 11: Mechanism of crack tip
blunting
Figure 12. Final stretch zone recognized after point B
in Fig. 11 for different regions in welded joint (see Table 1)
Table 1: Final stretch zones for weld metal and heat-affected-zone /14/
Sample
Position
Temperature Final stretch zone
1
Weld metal
20
°
C
0.14 mm
4
Heat-affected-zone 0.5 mm from fusion line
20
°
C
0.19 mm
8
Heat-affected-zone 0.2 mm from fusion line
-60
°
C
0.44 mm
9
Heat-affected-zone 0.5 mm from fusion line
-60
°
C
0.23 mm


















