
119
where
σ
YW
and
σ
YB
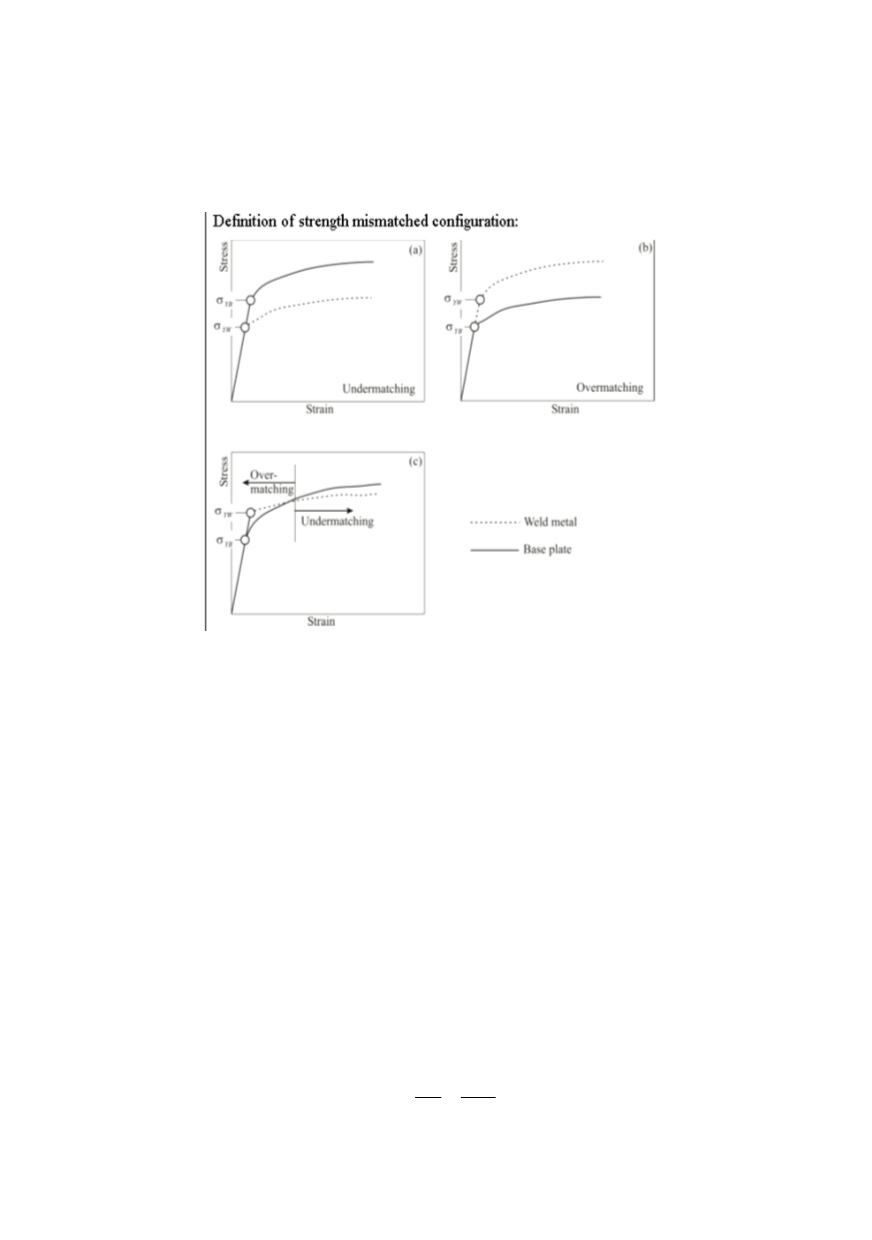
present the yield strength of the weld metal and of base metal, respec-
tively. The weld metal is commonly produced with yield strength higher than that of the
base plate; this is known as overmatching (OM) with the mismatch factor
M
> 1. An
increases use of high strength steels forces the fabricator to apply a consumable of lower
strength to comply toughness requirements, this is undermatching (UM),
M
< 1.
Figure 16: Strength mismatch definition /12/
The mismatch plays an important role for:
- fracture toughness of material (weld metal and base metal),
K
mat
,
J
mat
, CTOD
mat
;
- stress intensity factor solution (
K
I
) in linear-elastic and elastic-plastic ranges; and
- limit load solution given by appropriate terms, like plastic limit load
F
Y
.
Undermatching (UM) gives rise to a strain concentration in the weld metal, while
overmatching (OM) reduces the strain in the weld metal as compared to the base plate.
The SINTAP procedure offers separate assessment options for the analysis of such cases.
6.5. Plastic limit load
F
Y
The plastic limit load of the component with crack is one of the key parameters of the
SINTAP analysis. Limit load is a net section yield load which refers roughly to that load
of still unbroken ligament ahead of the crack is first fully plastic and the local load-
deformation curve becomes non-linear. In a fracture mechanics analysis it has to distin-
guish a plastic collapse load which is identical to the maximum load which the structure
with crack can sustain and a net section yield load. Within the SINTAP procedure a com-
pendium of limit loads is provided and a loading parameter
L
r
is used, defined as the ratio
of the applied load
F
and the limit load
F
Y
or respectively as the ratio of an applied net
section stress
σ
ref
and the yield strength of the material,
σ
Y
:
ref
Y Y
r
F L
F
σ
σ
= =
(6)


















