
115
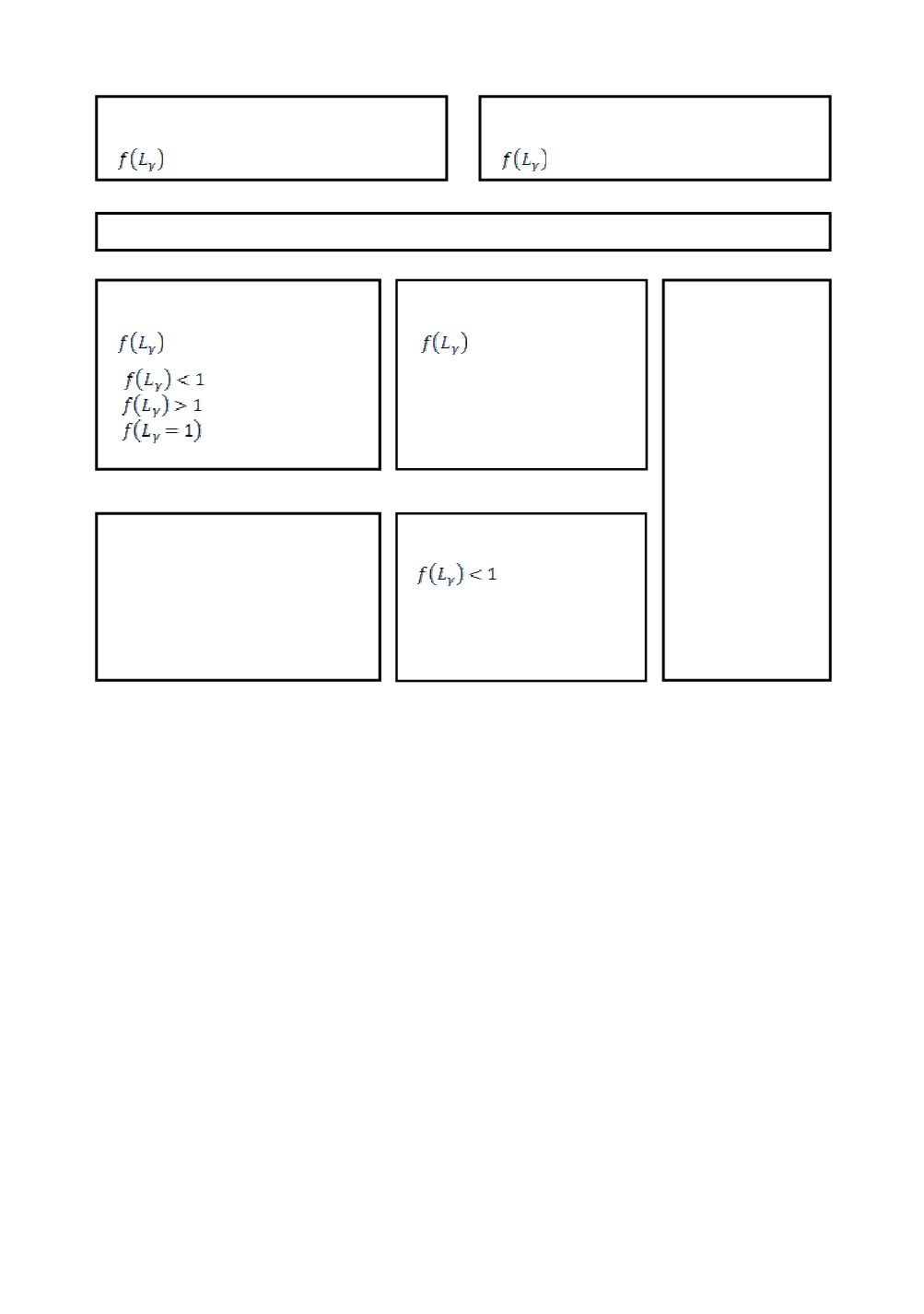
Figure 10: Analysis levels of the SINTAP procedure
In order to determine a critical crack size the following input data are required:
• Geometry and dimensions of the component,
• Applied loading including secondary load components, such as residual stress,
• Information on crack type and orientation, and
• The stress-strain curve and fracture toughness of the material.
6.1. Geometry and dimensions of the component
This data can be found in different handbooks. As an example, in Fig. 11 radial (a)
and longitudinal (b) cracks in a disk are presented.
6.2. Applied loading including secondary load components
The applied load can be introduced as:
- Single load such as a tensile force,
- Bending moment or
- Internal pressure.
Hence, the stress profiles over the thickness of primary,
σ
1
, and secondary,
σ
2
,
stresses, neglecting the effect of a crack and determined by a finite element analysis, are
presented in the Fig. 12.
SINTAP: Analysis Level 3
-alternatively CDF or FAD
-
continuous function
R6 Opt.1
-special option for strength
mismatch
(based
on
mismatch limit loads from
ETM-MM and R6, App. 16
SSS
Special Levels &
Options
-FE calculation
-Master curve
-Charpy testing
-Constraint
-Tearing analyses
-Leak-before break
-Pre-stress effect
-Reliability
S
SINTAP: Analysis Level 0
-alternatively CDF or FAD
-
(modified R6
Opt. 1)
-Toughness estimation from
Charpy energy
S
SINTAP: Analysis Level 2
-
alternatively CDF or FAD
-modification of Level 1, for
strength mismatch configurations
(based on mismatch limit loads
from ETM-MM an R6, App. 16)
S
SINTAP: Analysis Level 1
-
alternatively CDF or FAD
-
piecewise function
-
(modified R6 Opt.1)
-
(modified ETM)
-
(original equation)
R
R6-Routine
-
Basic concept: FAD
-
continuous function
E
Engineering Treatment Model (ETM)
-
Basic concept: CDF
-
piecewise function
S
SINAP (Structural Integrity Assessment Procedure for European Industry


















