
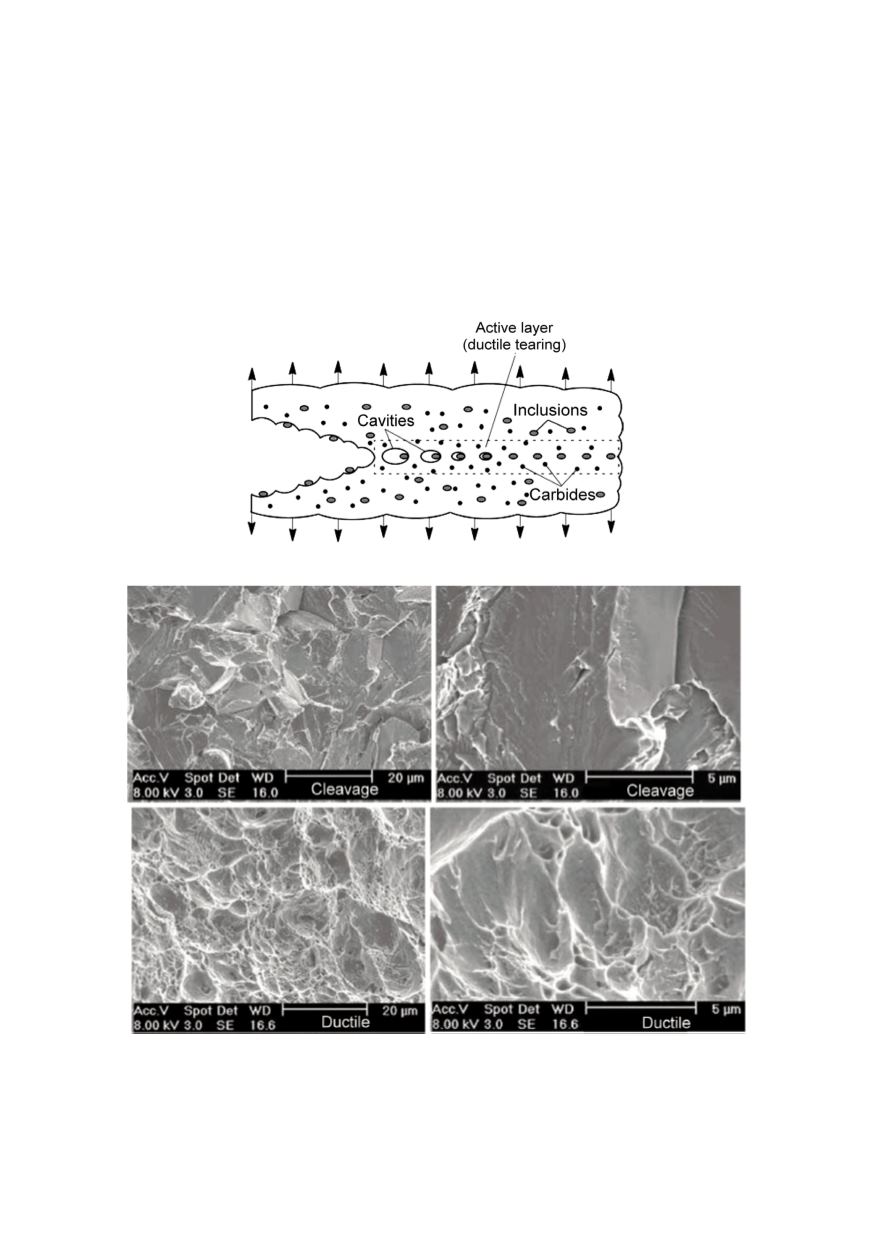
24
cavities grow and they coalescence. Final fracture took place when remain material
between the cavities breaks (tearing): the critical deformation necessary provokes the
cavities coalescence formed around the inclusions. The microvoid coalescence fracture
surface has a fibrous appearance based on tearing between the cavities. Figure 6
compares the appearances of two fracture types under the scanning electron microscope.
3. ELASTIC-PLASTIC FRACTURE MECHANICS (EPFM)
In the narrower sense, linear elastic fracture mechanics is applicable only for materials
that break in the fully brittle manner. However, almost all structural components are made
from materials of at least minimum ductility.
Figure 5: Phenomenology of ductile fracture
Figure 6: Fracture appearance (up fracture by cleavage; down by microvoid coalescence)
Treatment of the plasticity by EPFM falls into two main categories:
•
Simple correction of the LEFM theory under the conditions of small scale yielding on
the crack tip where the plastic volume is contained up to the fracture in elastic material.


















