
267
and is commonly produced with yield strength,
σ
YW
, greater than that of the base plate,
σ
YB
, the case is designated with the mismatch factor
YW
YB
M
σ
σ
=
(1)
Undermatching (M<1) gives rise to a strain concentration in the weld metal and it is
therefore good practice to avoid undermatching since the local ductility in the weld metal
can be exhausted at low global deformations. Overmatching (M>1) reduces the strain in
the weld material as compared to the base plate, thus shielding a defect in the weld metal.
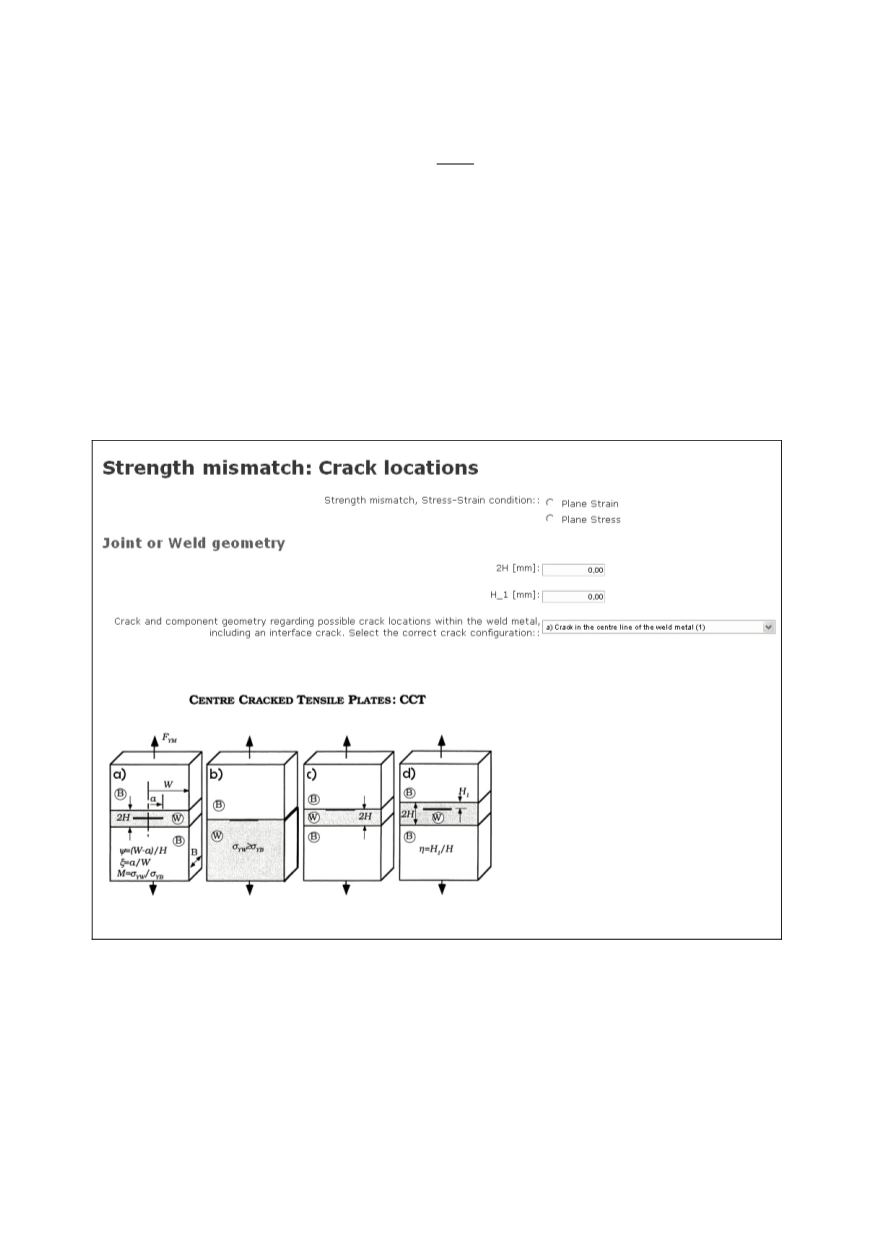
This option is only available if Strength mismatch is more than 10% (M<0.9 or
M>1.1). It is appearance depends on the selected configuration and normally requires the
following data (Fig. 7):
-
The stress-strain condition
-
Dimensions of the joint
-
Position of the crack according to the welding material
Figure 7: Crack location form (welded joints)
2.4. Material properties
The next step is to fill up the forms about the material properties.
2.4.1. Material # 1: Base
Several parameters are required accordingly to the selected procedure level, Table 1.
The dialog contains different fields to enable entering the material properties. There
are several options which depend on the level of SINTAP procedure. In addition to other


















