
17
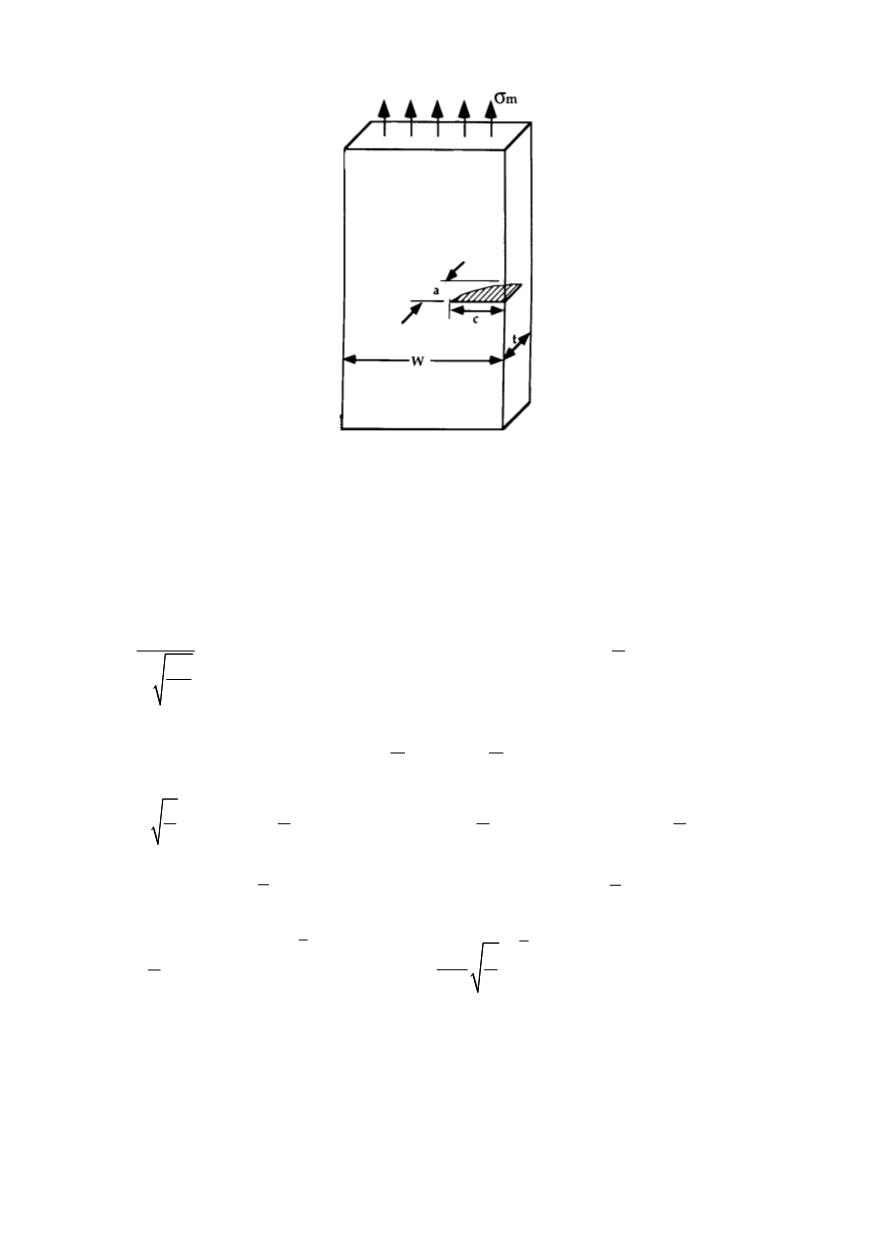
Figure 12: Model of tensile plate with an edge surface crack
For the evaluation of remote tensile stress
σ
(=
σ
m
),
necessary for the final fracture,
rectangular plate is assumed, of thickness
t
= 50 mm and width w = 135 mm in cross
section, through which contained semi-elliptic crack, 14x35 mm in size will propagate in
the material of plane strain fracture toughness
K
Ic
= 64.2 MPa
√
m.
The procedure based on linear elastic fracture mechanics for the angle position
φ
= 0
included following equations used in a sequence /4/:
m
K
a F
Q
σ
π
=
;
282.5
m
MPa
σ
=
(3)
1.65
1 1.464
1.323
c
Q
a
⎛ ⎞
= +
=
⎜ ⎟
⎝ ⎠
(4)
2
4
1
2
3
1 2
w
a
a
F M M M g g f f
t
t
ϕ
⎡
⎤
⎛ ⎞
⎛ ⎞
= +
+
⎢
⎥
⎜ ⎟
⎜ ⎟
⎝ ⎠
⎝ ⎠
⎢
⎥
⎣
⎦
(5)
1
1.08 0.03
0.69
c
c
M
a
a
⎡
⎤ ⎛ ⎞
=
+
= ⎜ ⎟
⎢
⎥
⎝ ⎠
⎣
⎦
;
2
2
0.375
0.06
c
M
a
⎛ ⎞
=
= ⎜ ⎟
⎝ ⎠
;
2
3
0.25
0.04
c
M
a
⎛ ⎞
= −
= −
⎜ ⎟
⎝ ⎠
(
)
2
3
1
1 0.08 0.4
1 sin 1.11
c
g
t
ϕ
⎡
⎤ ⎛ ⎞
= + +
−
=
⎢
⎥ ⎜ ⎟
⎝ ⎠
⎢
⎥
⎣
⎦
,
(
)
2
3
2
1 0.08 0.15
1 cos
1
c
g
t
ϕ
⎡
⎤ ⎛ ⎞
= + +
−
=
⎢
⎥ ⎜ ⎟
⎝ ⎠
⎢
⎥
⎣
⎦
1
2
4
2
2
sin cos
1
c
f
a
ϕ
ϕ
ϕ
⎡
⎤
⎛ ⎞ =
+
=
⎢
⎥
⎜ ⎟
⎝ ⎠ ⎢
⎥
⎣
⎦
,
1
2
sec
1
2
w
c a
f
W t
π
⎡
⎤
⎛
⎞
=
=
⎢
⎥
⎜
⎟
⎜
⎟
⎢
⎥
⎝
⎠
⎣
⎦
;
F
= 0.788
3.6. Conclusion
The examination and analysis of the carriage monoblock wheel fracture causes allows
the following conclusions:
- Fatigue crack emerged under the influence of cyclic stresses induced by braking and
is situated at the highest stress concentration location, chuck marks.


















