
169
Engineering procedure of Electric Power Research Institute
(
EPRI
)
In this procedure the analytical solutions for
J
integral, crack mouth opening and load-
line displacements are included, for elastic-plastic material behaviour of cylinders with
longitudinal and circumferential cracks, combining elastic and fully plastic regions /10/.
Ratwani-Erdogan-Irwin
(
REI
)
model
It deals with elastic-plastic analysis of a thin cylindrical shell with longitudinal crack,
neglecting transversal shear, and to allow derived integral equations /11/ simplify as
–
the shape of the crack is rectangular (crack depth
c
is a constant);
–
material ahead the crack tip is taken as perfectly plastic (no strain hardening), that
means it obeys Dugdale’s model.
Model REI can be applied to any crack type (through, part-through or surface
longitudinal crack) in cylindrical pressure vessel. Its main advantage is a simple use
because all the necessary data for calculation are in normalized form. Here, it is applied
for determining the crack driving force on welded joint of cylindrical vessels.
King’s model
It is based on the idea that a 3D problem can be solved by combing 2D problems of
plane stress and plane strain state. Namely, if through-thickness crack is in question, the
problem would be in 2D plane stress, and if the surface crack length is equal to the plate
width, the problem would be of plane strain type. Since surface crack is between these to
extreme cases, the solution can be found combining 2D problems. Plane stress problem
must consider local membrane force
N
and moment
M
, because of existence of ligament
length
t
-
c
, where
t
is plate thickness,
c
is crack depth /12/.
In fact, King’s model is a simplified line - springs model.
4. INTEGRITY ASSESSMENT OF PRESSURE VESSELS IN SERVICE
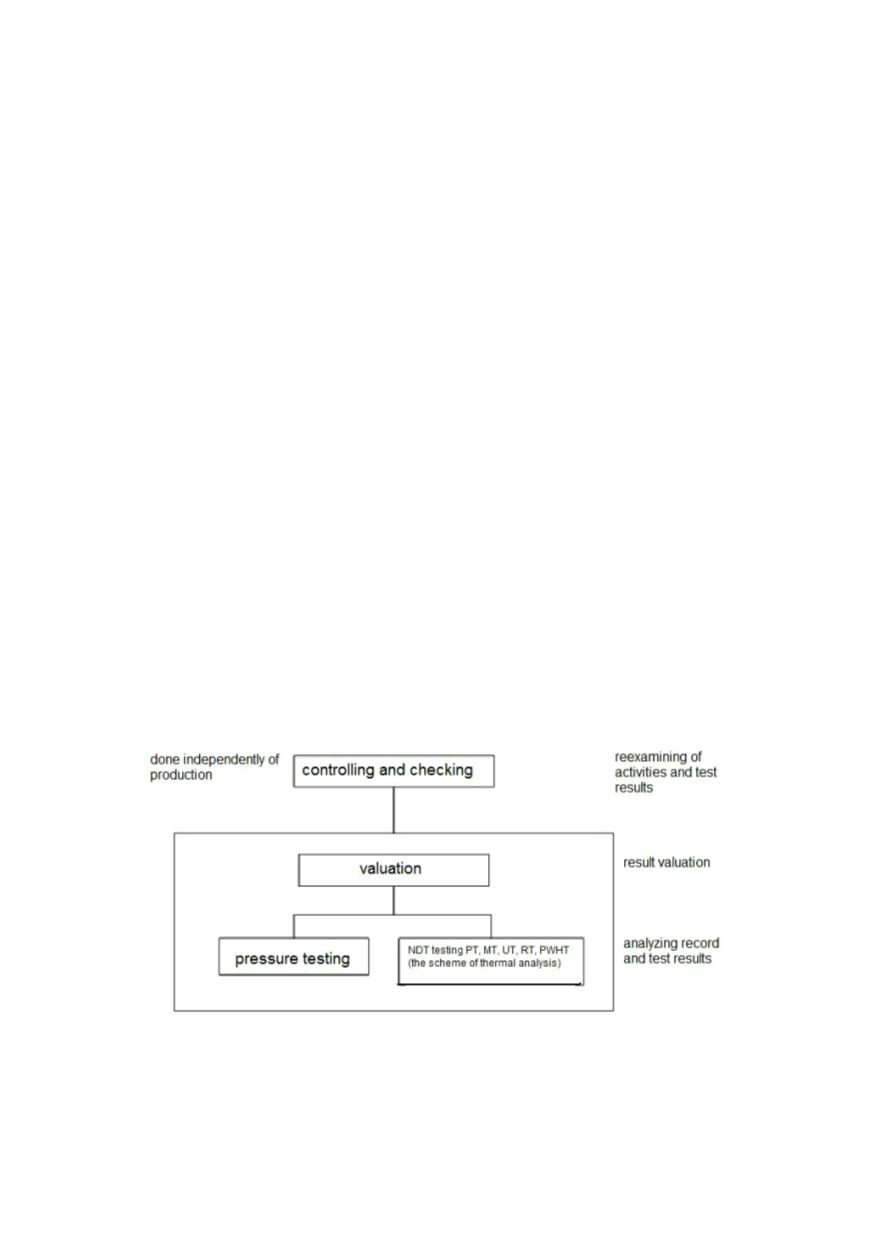
Figure 6 shows the scheme of activities in controlling and inspecting pressure vessels.
Integrity assessment of pressure vessels in service primarily depends on capability of
detecting and determining type, position and magnitude of imperfection in welded joints.
Figure 6: Examination activities and check-up scheme
Assessment of pressure equipment state in service applying NDT method can be
classified into eight different activities:
1.
Identification of labels
2.
Measurement of dimensions and their evaluation


















