
170
3.
Determining material chemical composition
4.
Determining material mechanical and physical characteristics
5.
Micro-structural characterization of material
6.
Detection of imperfections and assessment of their significance
7.
Leakage detection and evaluation of its significance
8.
Determining stress and dynamic response
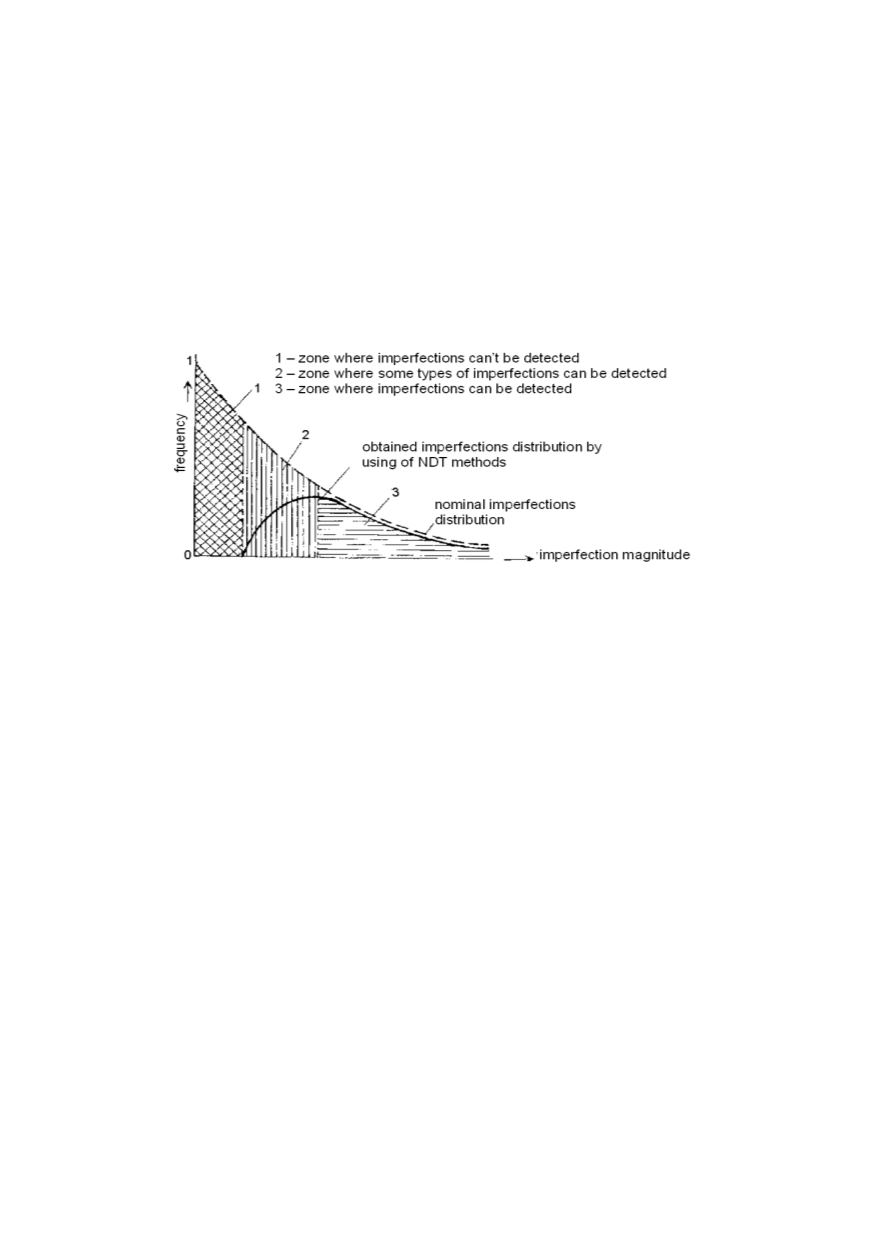
Selection of appropriate or combination of NDT methods demands full understanding
of problem, capacity and sensitivity of equipment, including skill and experience of
personnel. The relation between imperfection size frequency and capacity of NDT me-
thods is given in Fig. 7. Dye penetrant, magnetic particles and eddy current are mostly
used to detect surface cracks, radiographic and ultrasound methods for embedded defects.
Figure 7: Distribution of imperfection magnitude frequency related to capability of NDT methods
When imperfection is found, it is to decide whether it has to be removed or not, since
in case of welded joints imperfection presence does not mean explicitly loss of fitness for
purpose and use of welded structure, here pressure vessel. It is to analyze the imperfec-
tion type, its size and frequency relative to vessel class and load condition. The decision
should be made considering expected load, operating environment, the danger of fracture
and possible consequences. The approach which determines these factors is known as
“fitness for service” and has an advantage over experience indicators because:
–
repairs can be expensive, especially if the assembling and service are in delay;
–
the time for repair can be lower than the original production, since the repairs are often
performed by local removing of imperfections and re-welding; anyhow, repaired seam
can contain new defects, its toughness can be lower and residual stress can be
involved, because stress release heat treatment is usually inappropriate on a local level
and expensive for applying on a complex equipment.
Fitness-for-service in today’s practice presents a multi-process:
–
Imperfections have to be characterized in respect to size and position by NDT
methods and making decisions based on convenient assumptions.
–
Determining the local stress distribution.
–
Consideration of fatigue crack growth rate and the possibility of non-growing crack.
–
Determining imperfection critical size before fracture. If imperfection critical size will
be reached before next inspection, repair is necessary.
4.1. Pressure vessel modelling and calculation using Finite Element Method
Cylindrical horizontal welded storage tank (Fig. 8) from the manufacturing program of
“GOŠA FOM” company falls in group of transportable vessels. It is designated for the


















