
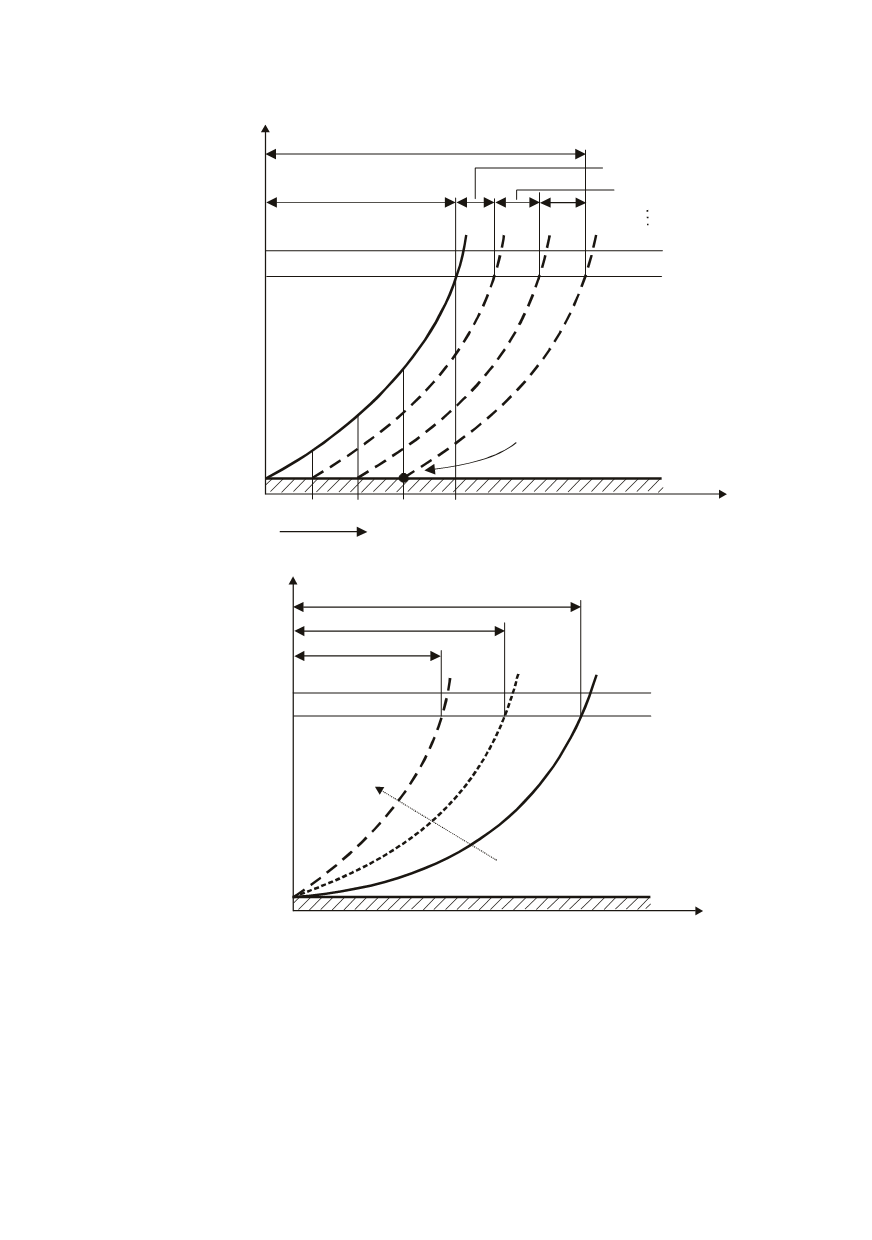
112
inspection 0. 1. 2. . m. time
i
crack detected
crack growth law
DLF
new design life time with crack
1. extension
2. extension
a
crit
80%
a
crit
Crack size parameter
a = a = a
min 0
NDI
Figure 5: Extension of service life time until the crack is not detected
a
crit
80%
a
crit
Crack size parameter
a = a = a
min 0
NDI
DLF
1
DLF
2
DLF
3
Materijal
degradation
Crack growth law
time
Figure 6: Effect of material properties degradation or wall thinning on service lifetime
However, the proposed principles are also applicable for materials of dropped
properties when the risk of the structural failure is not increased. On the basis of the
performed testing, it is possible to assess new values of critical crack lengths and new
service lifetime limited by the safety factor of reliable structure use. New stress analysis
is not required, if the results are available from the 1st stage (Fig. 7) and the wall thinning
is negligible. Therefore, only in a case, where the geometry (e.g. thickness of component
exposed to corrosion) changes should stress analysis be performed.


















