
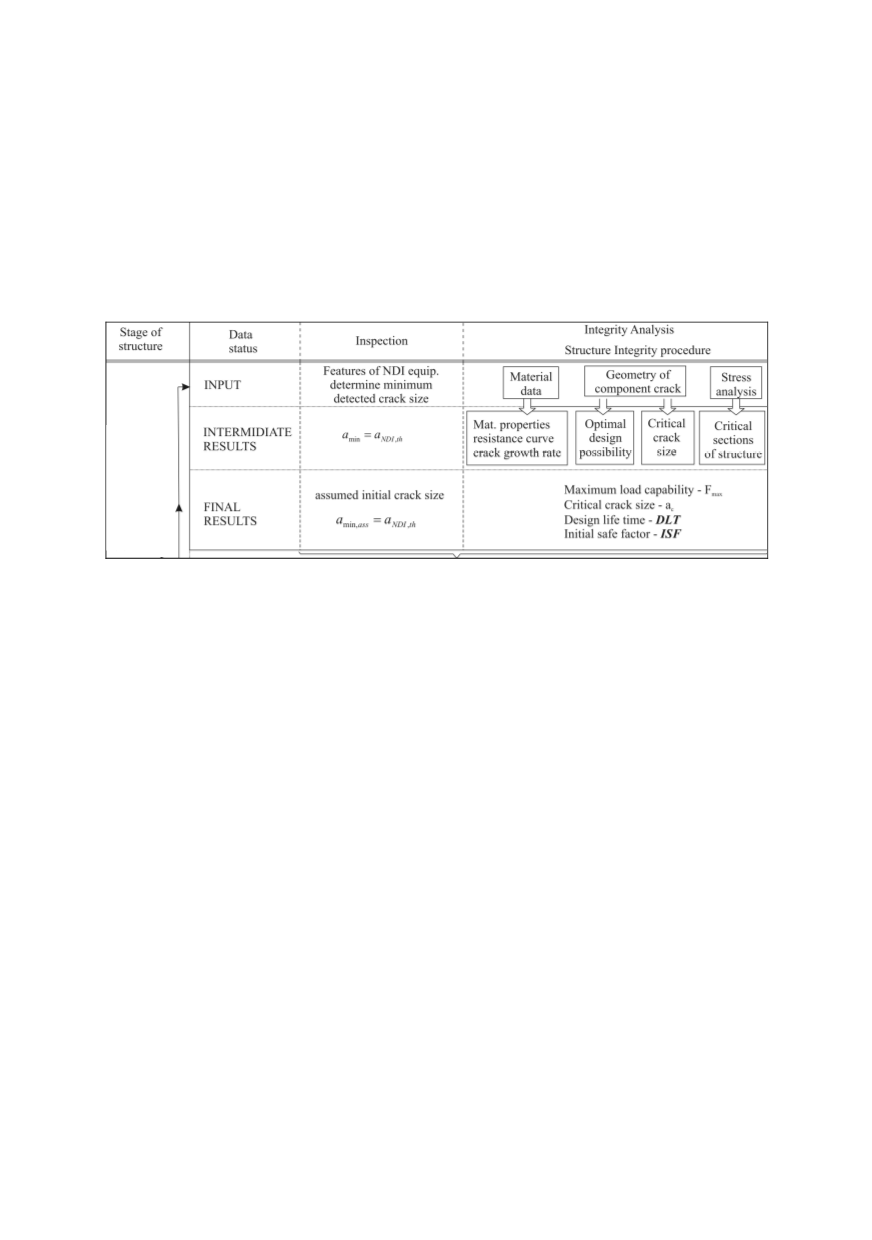
110
The results of this stage can be expressed in following data:
- The postulate assumed crack size,
- The maximum loading capacities of the structures,
- The servicing critical crack size,
- Design lifetime.
- Initial safety factor.
Next analysis, using these data, should give the answers to the following questions:
- Is calculated design lifetime (DLT) longer than the required design lifetime (RDLT)?
- Is initial safety factor (ISF) greater or equal to the required safety factor (RSF)?
Algorithm for this procedure is presented in the Fig. 3.
Figure 3: Algorithm for design lifetime estimation of a structure
In the case that the answers to both mentioned questions are positive, it is justifiable to
continue to the next step, to the manufacturing of a structure. It is also desirable to opti-
mize the design, e.g. to reduce the weight of a structure, if possible.
In the case of negative answers, the optimization is obligatory and the complete
procedure has to be repeated. Optimization generally includes:
- Selection of NDT equipment of higher quality;
- More complete data about material properties, or
- Selection of more suitable materials, and
- Redesign of structure.
4. MANUFACTURING STAGE
Parallel to the structural manufacture, it is necessary to make an NDI plan with a
reliable number of inspections during service (Fig. 4). The initial inspection NDI (“0”) is
necessary immediately after the manufacturing or assembling of a structure, as the initial
usage of the structure. During structural manufacture, the specimens for mechanical and
fracture-mechanical testing are necessary (Fig. 4). These specimens should be subjected
in testing to the same loading and environmental conditions as critical structural compo-
nents are exposed to in service. This procedure is already well-established in the nuclear
power plant industry.
During the exploitation NDI plan should foreseen at least 3 inspections during the
lifetime of structure. It is also desirable, for responsible structures, that critical location be
continuously monitored, applying convenient system by strain gauges, or introducing the
system of new generation, which includes up-dated devices based on television recording
and corresponding computer analysis.
DESIGN
New analysis is required


















