
83
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
initial crack length
a
0
= 10.4 mm
Experiment
CGM
initial crack length
a
0
= 8 mm
WM 6
F [kN]
CTOD [mm]
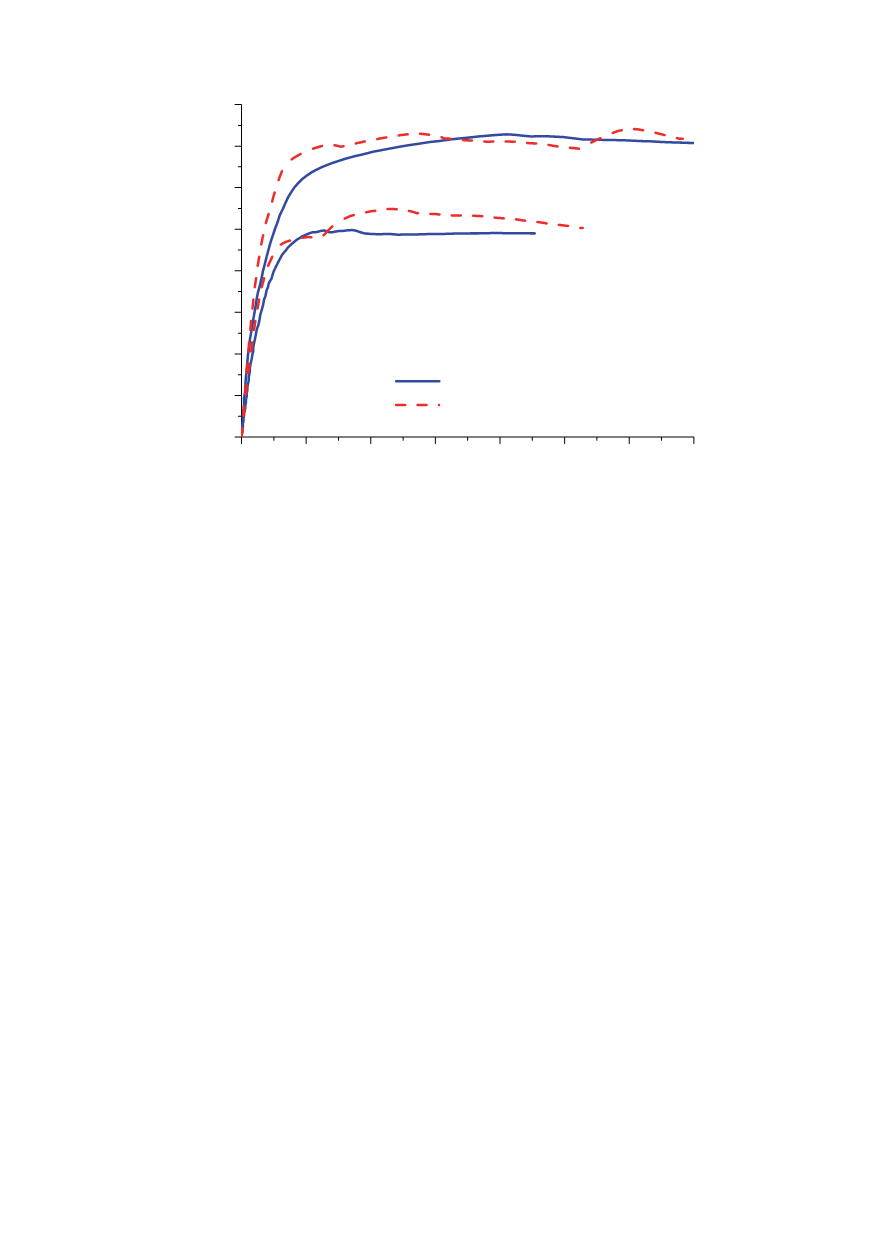
Figure 16:
F
-CTOD curves obtained experimentally and using the CGM for joint width 6 mm and
different initial crack lengths
6. CONCLUSIONS
An overview of the uncoupled and coupled micromechanical models of local approach
to ductile fracture has been given in this lecture. One of the coupled models, the complete
Gurson model, has been used for analysis of ductile fracture initiation in overmatched
welded joints made of high-strength low-alloyed steel of yield strength 545 MPa. SENB
specimens have been investigated. Metallographic observation has been used to quantify
the volume fraction of non-metallic inclusions
f
v
and mean free path between the
inclusions
λ
in the base metal and weld metal. Initial void volume fraction
f
0
has been set
as equal to
f
v
. CTOD at the moment of the crack growth initiation on SENB specimen has
been measured experimentally and calculated using the local approach.
It is found that the CGM enables determination of the crack growth initiation in
analysed welded joints. Damage parameter distribution exhibits only local character near
the crack tip, but the size of finite elements strongly influences the results. In addition, the
effect of integration order of the elements exists, while the interpolation order of the
element (quadratic or linear) does not influence the results significantly.
Analysis of the stable crack growth has shown that the loss of load-carrying capacity
of the material in the ligament due to the crack growth can be assessed using the CGM.
The results have been obtained by observing the damage in the elements along the crack
line, without releasing the nodes. The influence of the joint width is predicted correctly,
except for the widest joint, that exhibit certain deviations on force - crack tip opening
displacement diagram. The influence of the crack length can also be estimated using the
CGM. Nucleation of secondary voids around Fe
3
C particles doesn’t affect the behaviour
of the joints, because the percentage of carbon in the weld metal is rather low.


















