
189
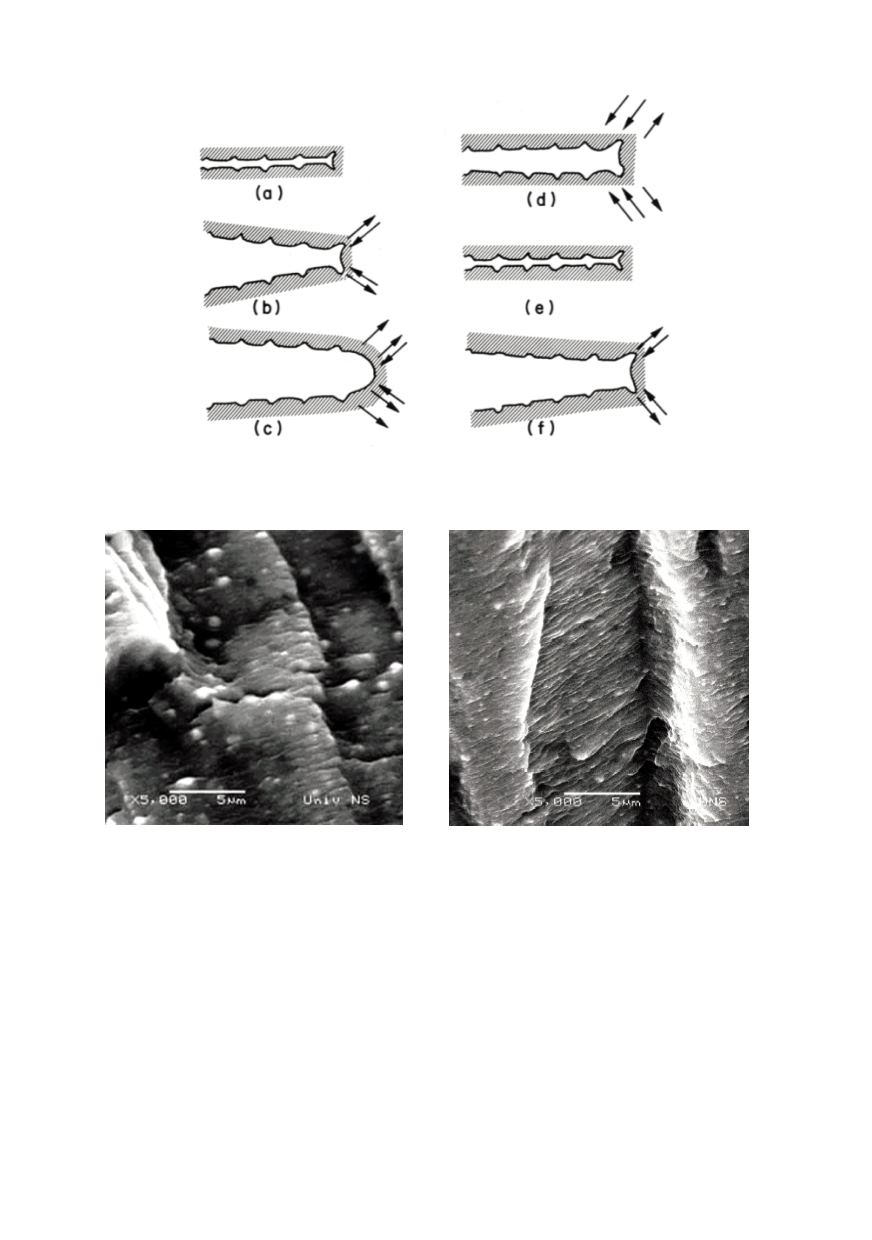
Figure 18: The crack blunting mechanism for striation formation during fatigue crack growth /13/
a.
b.
Figure 19: Fractographs fatigue fracture surface of 7000 aluminium alloys on SEM /14/
9. CONCLUDING REMARKS
T
he type of fracture caused by load application depends on the stress state on the
crack tip. When the plastic zone on the crack tip is small, as considered in LEFM, a
cleavage fracture occurs, whereas a ductile fracture occurs when the plastic zone on the
crack tip is large, considered in EPFM, producing different fracture morphology.
The width of the stretch zone when testing fracture toughness in EPFM conditions
provides a useful parameter for determination of J integral. The J value obtained by
measuring SZW is considered not to have
ligament size effect.
It must be taken into
account that the slope of the blunting line is sensitive to the microstructure and the
loading rate, and for that it is better to determine both width (SZW) and depth (SZD) of
stretch zone.


















