
225
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS MODIFICATION IN THE
MECHANICAL STRUCTURES REANALYSIS
Nataša Trišović
University of Belgrade, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Belgrade, Serbia
ntrisovic@mas.bg.ac.rs1. INTRODUCTION
Dynamic response of mechanical systems depends of structural parameters. In
mechanical structures reanalysis objective is to evaluate the structural response for
successive modifications in the design avoiding the difficult solution of the modified
equations. The structural modifications may be required by external factors or by the
designer in order to improve the characteristics of structure response (eigenvalues and
eigenvectors). Modification of dynamic characteristics means change of corresponding
design variables to get desired dynamic behaviour of a structure. The design variables
depend on the type of optimization problem. In the design of structural components, such
as stiffened panels and cylinders, the design parameters represent the size and shape of
stiffeners and their spacing, and the plates or shell thickness. The thickness of plates,
cross-section areas of bars, and areas, moments of inertia, and torsion constants of beams
represent the values which should be considered for modification. Joints and members
could be eventually added or exuded during reanalysis process, modifying in this way the
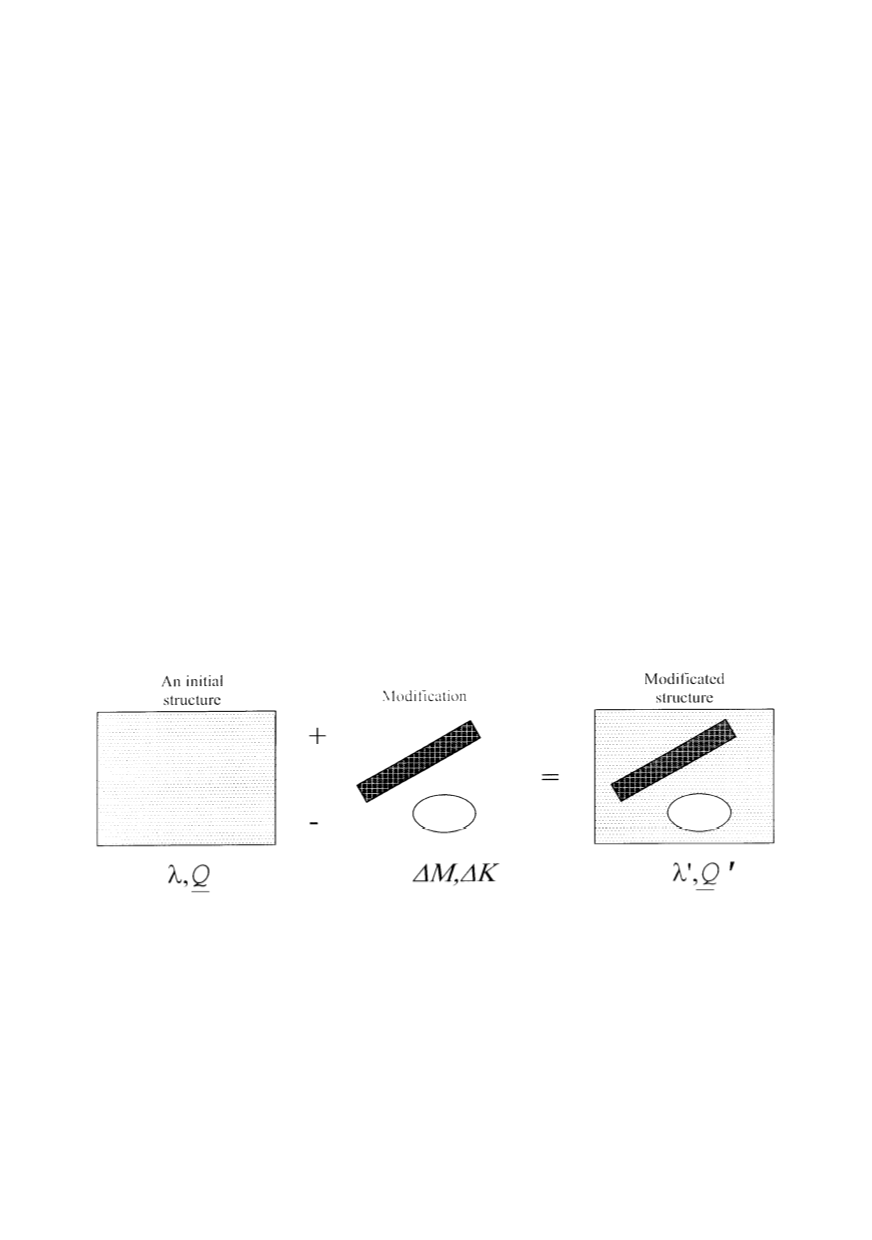
geometry of the structures. A simple scheme of dynamic modification during reanalysis is
presented in Fig. 1.
Figure 1: A simplified scheme of dynamic modification
Reanalysis methods might include following activities:
(a) Modification in the geometry, with no further change in the number of degrees of
freedom.
(b) Modification of design variables (mass, damping and stiffness).
(c) Increase or decrease of the number of degree of freedom (DOF) by changing the
supporting system, and addition or deletion of joints and members.
(d) Selection of new material for critical components, if possible.
Reanalysis methods mostly cannot involve the last two modifications, because they
imply a change in the dimension of the system due to addition or deletion of degrees of


















