
251
The examples of EMAT application are: monitoring of the billet temperature during
continuous casting of steel, on-line measurement of the wall thickness of seamless steel
tubing, inspection of buried gas pipelines, flaw detection by special wave modes in plates,
pipes and bars, long range inspection of railroad tracks, inspection of pipes by guided,
circumferential waves, inspection of piping using axial propagating transversal wave,
which can reach very long distances through the pipe wall, and many others.
Other application of EMAT is residual stress measurement in railroad wheels /12/
(acoustoelastic stress measurements). It is also used for high temperature measurements,
bolt-axial stress and grain-size measurements, monitoring fatigue and creep, surface flaw
detection, corrosion detection, long-range detection of flaw in wires.
3.2. Magnetic particle testing methods
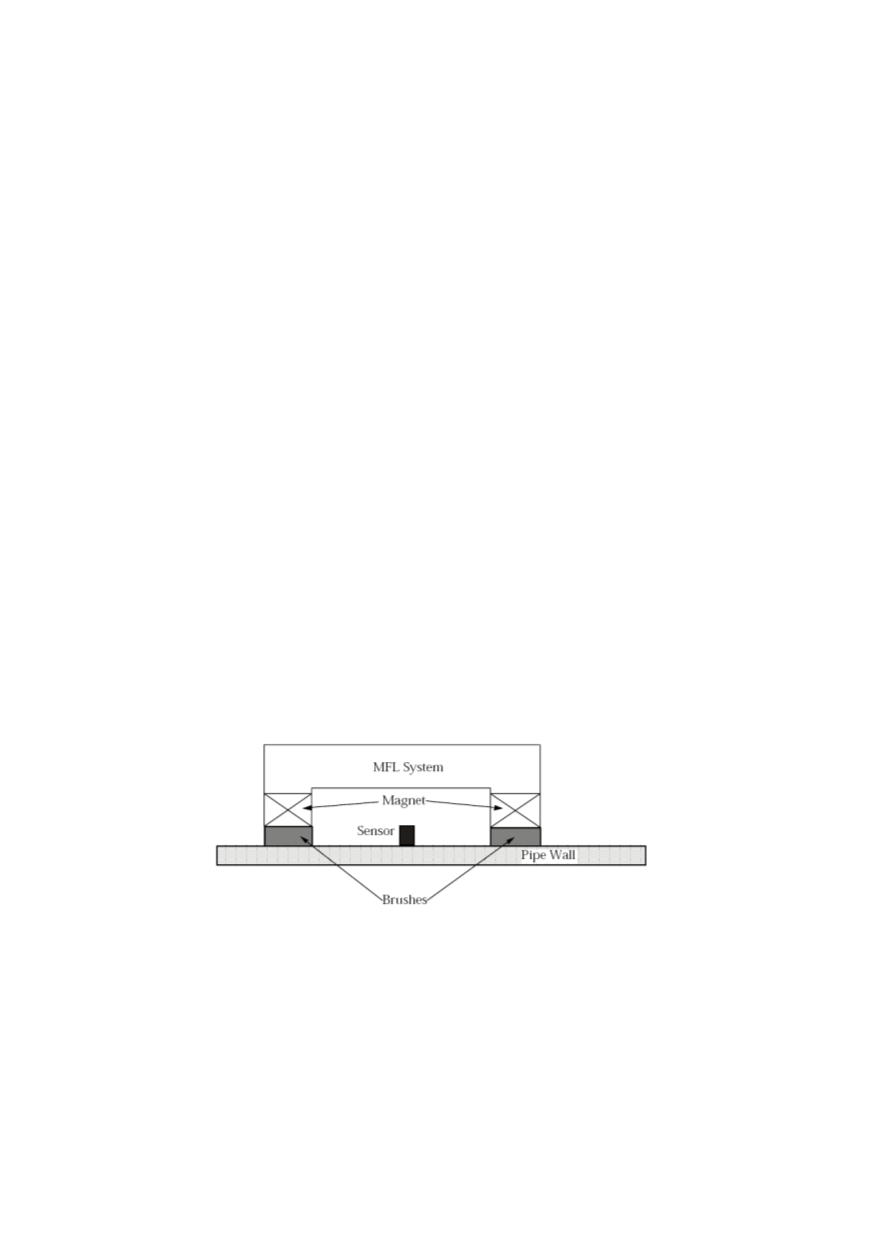
Besides UT, for surface and subsurface cracks detection the magnetic particle testing
(MT), Fig. 10, is in permanent use. MT is based on magnetic flux leakage. Liquid particle
MT is found to be more sensitive then dry particle MT. Both can use fluorescent particles
when black light is required.
For NDT of pipes made of broadly applied low alloyed steels are, MT magnetic flux
leakage methods, and UT, contact and contactless methods.
The measured flux leakage in MT is dependent on material properties, wall thickness,
stress in pipeline, and flaw size. Induction coil method and Hall sensor method are used.
The equipment for the MT method is known as pipe scan. It is an easy to use, cost
effective, portable, magnetic flux leakage inspection system for the detection of random
internal corrosion in pipes. The special, advanced magnetic material coupled with unique
mechanical design enable coverage of all pipe diameters from 50 mm to 2.4 m, with a
limited number of scanning heads. Unlike some inspection methods, magnetic flux is not
affected by fluid streaming through the pipeline, so surveys can be carried out both on-
line and off-line. Use of pipe scan of high probability of detection, to locate actual
internal corrosion, coupled with A scan ultrasonic monitoring of corrosion growth,
provides a cost effective accurate system for the determination of piping integrity.
Figure 10: The estimation of the size of surface cracks using Hall sensor
Applicable contact ultrasonic methods are piezoelectric (PET), shear and Lamb wave
techniques, and for contactless testing EMAT, magnetostrictive sensor, longitudinal,
shear wave and Lamb wave techniques are used.
3.3. Special applications of ultrasonic and magnetic particle testing methods
One of popular UT technique is long range ultrasonic testing. It has been introduced
commercially in early 1998 for the in-service monitoring of pipes and pipelines. It is
predominantly used by the oil and gas industry for detection of corrosion and other metal


















