
239
the basic condition under which they can work. In addition, when the measurements in
different measuring points are not synchronous, it is difficult to measure large
displacement and to get the observations in real time. The measurement by laser
interferometer is used to measure the distance changes between the measurement point
and the reference point. To achieve this goal, a prism or reflective film must be mounted
at the measurement point. The distance change versus time can be collected and be
further analysed to determine dominant frequencies and corresponding amplitudes. This
method offers high accuracy, but it is difficult to catch the measurement point when
structure vibrations or shake are too expressed. So, all these traditional methods are of
limited capacity regarding continuity, real time and automatization for monitoring large
structures in real conditions
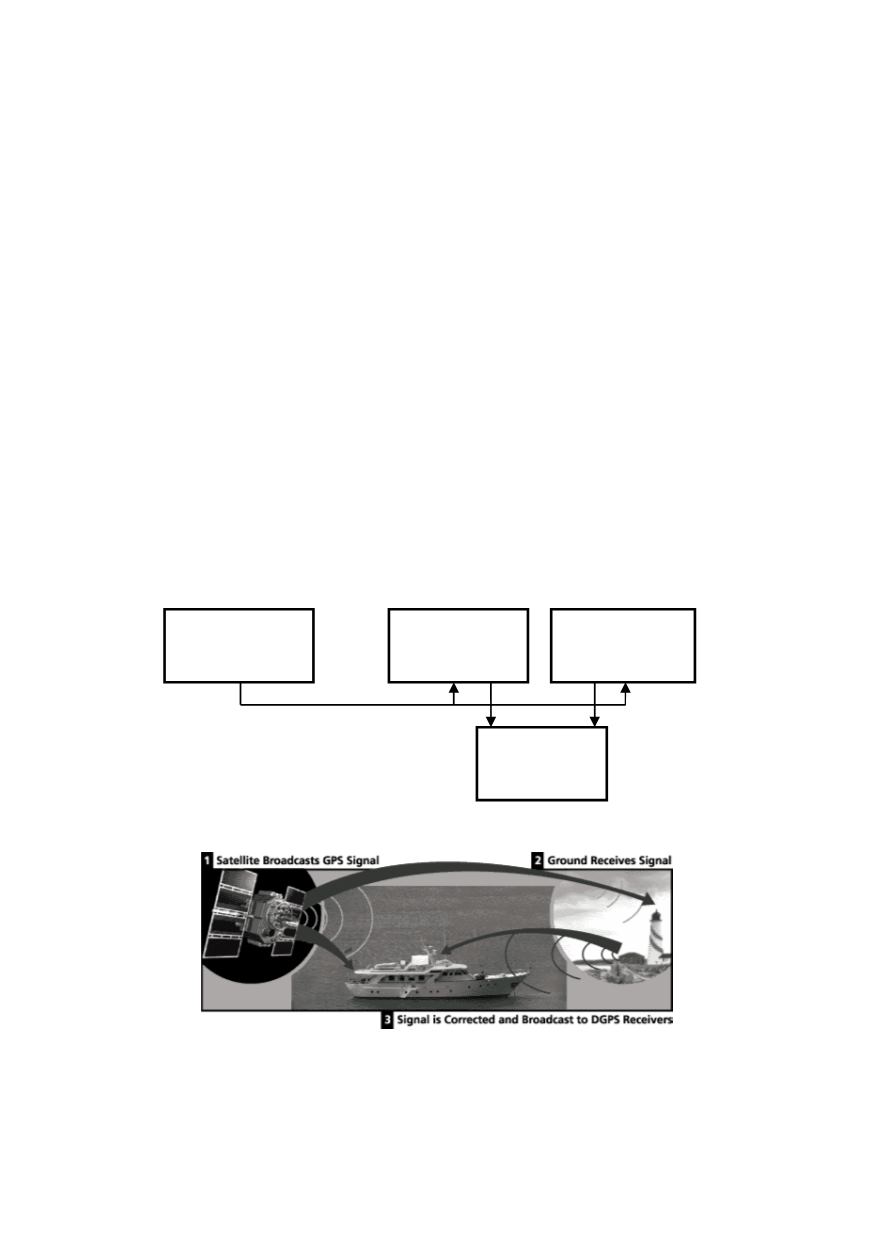
A GPS system also includes communication elements and monitoring center, Fig. 1. A
GPS reference station tracks all GPS satellites that are in view at its location, and all
antennas in remote stations simultaneously receive satellite signals from several satellites.
A GPS receiver must be locked on to the signal of at least three satellites to calculate a
2D position (latitude and longitude) and track movement. With four or more satellites in
view, the receiver can determine the user's 3D position (latitude, longitude and altitude).
At the reference station, the difference information is generated and transmitted to the
remote stations in real time. In the remote station, the signal received from the satellites is
corrected by the difference information from the reference station. The remote 3D
coordinates of a station are calculated in real time using Differential GPS (DGPS)
software, Fig. 2. The coordinates are then transmitted to the GPS monitoring center and
are further processed so as to get the displacements of a structure in three directions.
Figure 1: Simplified block scheme of GPS monitoring system
Figure 2: The scheme of the Differential GPS (DGPS)
Once the user's position has been determined, the GPS unit can calculate other
information, such as speed, bearing, track, trip distance, distance to destination. Each of
those timing signals is going to have some error or delay depending on what sort of perils
GPS Reference
Station
GPS Remote
Station 1
GPS Remote
Station n
Monitoring
center


















